1. Ultimate Guide To Perfecting Weather Predictions Now
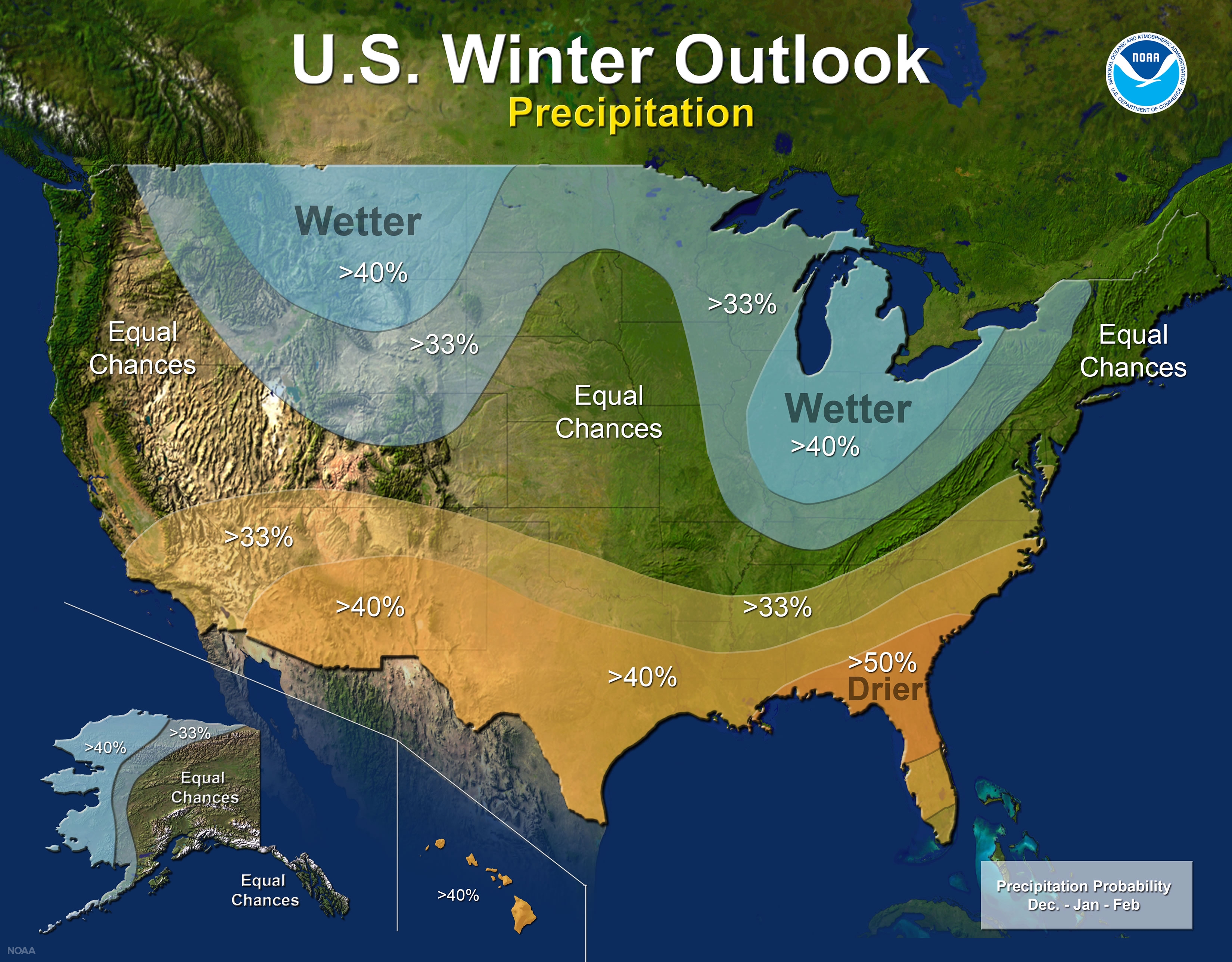
Introduction to Weather Prediction

Weather prediction is an intricate science that has come a long way, empowering us to forecast and anticipate the ever-changing conditions of our atmosphere. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various techniques, technologies, and considerations that contribute to accurate weather forecasting. From understanding the fundamentals to exploring advanced methodologies, we aim to provide you with a deep understanding of the art of weather prediction.
Understanding the Basics of Weather Forecasting

Before we dive into the intricacies of weather prediction, let’s grasp the fundamentals. Weather forecasting involves analyzing and interpreting various atmospheric conditions and patterns to make informed predictions about future weather events. It is a complex process that requires a combination of scientific knowledge, technological advancements, and skilled interpretation.
Key Components of Weather Forecasting
Atmospheric Conditions: Weather forecasting heavily relies on monitoring and understanding atmospheric conditions such as temperature, humidity, air pressure, wind speed and direction, and cloud formation. These factors play a crucial role in shaping the weather patterns we experience.
Weather Models: Sophisticated computer models are utilized to simulate and predict weather patterns. These models take into account vast amounts of data, including atmospheric conditions, topography, and even ocean currents, to generate accurate forecasts.
Observation and Data Collection: Weather forecasting relies on a vast network of observation stations, satellites, and weather balloons to collect real-time data. This data is crucial for validating and refining weather models, ensuring their accuracy.
Meteorological Analysis: Skilled meteorologists play a vital role in interpreting weather data and models. They analyze patterns, identify trends, and make informed predictions based on their expertise and experience.
The Evolution of Weather Prediction

Weather prediction has evolved significantly over the years, thanks to advancements in technology and our understanding of atmospheric processes. Let’s explore some key milestones in the evolution of weather forecasting:
Traditional Methods
In ancient times, people relied on natural indicators and traditional wisdom to predict weather patterns. Observing the behavior of animals, the position of stars, and even the appearance of certain plants were used as indicators of upcoming weather conditions. While these methods lacked scientific precision, they provided a basic understanding of seasonal changes.
The Birth of Modern Weather Prediction
The modern era of weather prediction began in the 19th century with the development of meteorological instruments and the establishment of weather observation networks. The invention of the thermometer, barometer, and anemometer revolutionized weather data collection, allowing for more accurate measurements and observations.
In the late 19th century, the concept of weather forecasting gained momentum with the work of British meteorologist Sir Francis Galton. He introduced the idea of using statistical techniques to analyze weather patterns and make predictions. This laid the foundation for the quantitative approach to weather forecasting.
The Rise of Computer Models
The mid-20th century marked a significant turning point with the introduction of computer models in weather prediction. These models, known as Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP), revolutionized the field by allowing for the simulation of complex atmospheric processes. By feeding vast amounts of data into these models, meteorologists could generate more accurate and detailed forecasts.
Advances in Technology
The latter half of the 20th century witnessed rapid advancements in technology, further enhancing weather prediction capabilities. The launch of weather satellites provided a global perspective on atmospheric conditions, enabling more precise monitoring and forecasting. Additionally, the development of supercomputers allowed for the processing of massive datasets, improving the accuracy and resolution of weather models.
Modern Weather Prediction Techniques

In today’s world, weather prediction has become an intricate and highly specialized field. Let’s explore some of the advanced techniques and technologies used in modern weather forecasting:
Satellite Imagery and Remote Sensing
Satellite imagery plays a crucial role in weather prediction by providing a bird’s-eye view of atmospheric conditions. Advanced satellites equipped with various sensors capture detailed images of cloud formations, temperature profiles, and even atmospheric moisture content. This data is invaluable for meteorologists in identifying developing weather systems and making accurate forecasts.
Radar Technology
Weather radar systems have become an indispensable tool in weather forecasting. These systems use electromagnetic waves to detect and track precipitation, such as rain, snow, and hail. By analyzing the reflected signals, meteorologists can determine the intensity, movement, and structure of weather systems, aiding in short-term forecasting and severe weather warnings.
Data Assimilation and Ensemble Forecasting
Data assimilation is a critical process in weather prediction, where real-time observations are combined with model simulations to create the most accurate forecast possible. Ensemble forecasting takes this a step further by running multiple simulations with slightly different initial conditions. This approach helps meteorologists understand the range of possible outcomes and increases the reliability of forecasts.
High-Resolution Weather Models
Advancements in computing power have led to the development of high-resolution weather models. These models use finer grid sizes, allowing for more detailed simulations of atmospheric processes. As a result, meteorologists can generate forecasts with increased spatial and temporal resolution, providing more accurate predictions for localized areas.
Factors Affecting Weather Prediction Accuracy

While weather prediction has come a long way, there are still several factors that can impact the accuracy of forecasts. Understanding these factors is crucial for interpreting and utilizing weather predictions effectively.
Data Quality and Availability
The quality and availability of weather data play a vital role in the accuracy of forecasts. Inadequate or incomplete data can lead to inaccurate simulations and predictions. Meteorologists rely on a vast network of observation stations, satellites, and other data sources to ensure the availability of high-quality data.
Complexity of Atmospheric Processes
The atmosphere is a highly complex and dynamic system, with numerous interconnected processes influencing weather patterns. From the formation of clouds to the interaction of air masses, these processes can be challenging to model accurately. Meteorologists continuously refine and improve weather models to better represent these complexities.
Model Limitations and Uncertainty
Weather models, despite their sophistication, still have limitations and uncertainties. Factors such as model resolution, initial conditions, and the representation of certain atmospheric processes can introduce errors and biases. Meteorologists employ various techniques, such as ensemble forecasting, to quantify and mitigate these uncertainties.
Interpreting Weather Forecasts

Understanding how to interpret weather forecasts is essential for making informed decisions. Let’s explore some key considerations when analyzing weather predictions:
Forecast Confidence and Uncertainty
Weather forecasts often come with a level of confidence and uncertainty. Meteorologists use statistical techniques to assign confidence levels to different aspects of the forecast, such as temperature, precipitation, or wind speed. Understanding these confidence levels helps users assess the reliability of the forecast.
Short-Term vs. Long-Term Forecasts
Weather forecasts can vary in their temporal range, from short-term predictions for the next few hours to long-term forecasts spanning several days or even weeks. Short-term forecasts tend to be more accurate, as they rely on real-time data and have a smaller window of uncertainty. Long-term forecasts, on the other hand, are more challenging and rely on a combination of model simulations and historical patterns.
Localized Forecasts
Weather conditions can vary significantly over short distances, especially in regions with complex topography or coastal influences. Localized forecasts, which provide detailed information for specific areas, are crucial for activities such as outdoor events, agriculture, or transportation planning. These forecasts take into account local microclimates and can provide more accurate predictions for specific locations.
Weather Prediction in Different Regions
Weather prediction techniques and challenges can vary depending on the region and its unique atmospheric conditions. Let’s explore how weather forecasting differs in various parts of the world:
Tropical Regions
Tropical regions, characterized by their warm and humid climates, present unique challenges for weather prediction. The complex interplay of moisture, convective processes, and the formation of tropical cyclones requires specialized models and expertise. Meteorologists in these regions often focus on tracking and forecasting the movement of tropical storms and hurricanes.
Polar Regions
Weather prediction in polar regions, such as the Arctic and Antarctic, faces distinct challenges due to the extreme cold and the presence of sea ice. The complex interactions between the atmosphere, ocean, and sea ice make it difficult to accurately model and predict weather patterns. Specialized models and observation networks are employed to monitor and forecast weather conditions in these remote and sensitive regions.
Coastal Areas
Coastal areas are influenced by both land and sea, leading to unique weather patterns. The proximity to the ocean can result in rapid changes in weather conditions, such as the formation of sea breezes or the occurrence of fog. Meteorologists in coastal regions need to consider the impact of ocean currents, tides, and coastal topography on weather systems.
Weather Prediction for Different Applications

Weather prediction serves a wide range of applications, each with its own specific requirements and challenges. Let’s explore how weather forecasts are utilized in various fields:
Agriculture and Food Security
Accurate weather forecasts are crucial for agriculture, as they help farmers make informed decisions about planting, irrigation, and pest control. Long-term forecasts can provide valuable insights into seasonal weather patterns, allowing farmers to plan their crop cycles and manage resources effectively. Weather predictions also play a role in food security by helping to anticipate and mitigate the impact of extreme weather events on agricultural production.
Transportation and Aviation
Weather conditions can significantly impact transportation systems, including road, rail, and aviation. Real-time weather forecasts are essential for ensuring the safety and efficiency of transportation networks. Severe weather warnings, such as heavy rain, snow, or strong winds, can prompt the implementation of emergency protocols and alter travel plans. Accurate weather predictions are particularly critical for aviation, as they help pilots navigate around hazardous weather conditions and ensure the safety of passengers.
Energy Production and Management
Weather forecasts play a vital role in the energy sector, particularly for renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power. Wind speed and direction, as well as solar radiation levels, are key factors in determining the availability and output of these energy sources. Accurate weather predictions help energy producers optimize their operations, balance the grid, and ensure a stable supply of renewable energy.
Emergency Management and Disaster Response
Weather forecasts are crucial for emergency management and disaster response efforts. Severe weather events, such as hurricanes, floods, or wildfires, can have devastating impacts on communities. Accurate and timely weather predictions allow emergency responders to prepare and respond effectively, saving lives and minimizing damage. Meteorologists work closely with emergency management agencies to provide critical weather information and support decision-making during crisis situations.
Enhancing Weather Prediction Accuracy

While weather prediction has made significant strides, there is always room for improvement. Researchers and meteorologists continuously work on enhancing the accuracy and reliability of forecasts. Here are some ongoing efforts to improve weather prediction:
Advancements in Model Development
Meteorologists and researchers are dedicated to refining and improving weather models. This involves incorporating new scientific understanding, enhancing model resolution, and incorporating advanced techniques such as machine learning and artificial intelligence. By constantly updating and optimizing models, meteorologists aim to reduce uncertainties and improve forecast accuracy.
Collaboration and Data Sharing
Collaboration between meteorologists, researchers, and weather organizations is essential for advancing weather prediction. By sharing data, expertise, and best practices, the community can collectively enhance forecasting capabilities. International collaborations, such as the World Meteorological Organization, facilitate the exchange of knowledge and resources, leading to more accurate and consistent weather forecasts on a global scale.
Public Engagement and Feedback
Engaging with the public and gathering feedback is crucial for improving weather prediction services. Meteorologists and weather organizations often seek input from users to understand their needs and preferences. By incorporating user feedback, forecasts can be tailored to meet specific requirements and provide the most relevant and useful information.
Conclusion

Weather prediction is a fascinating and ever-evolving field, combining scientific knowledge, technological advancements, and skilled interpretation. From ancient wisdom to modern computer models, the journey of weather forecasting has been remarkable. As we continue to refine our understanding of atmospheric processes and leverage cutting-edge technologies, the accuracy and reliability of weather predictions will only improve.
Stay tuned for future advancements in weather prediction, as meteorologists and researchers strive to provide even more accurate and detailed forecasts. By staying informed and utilizing weather predictions effectively, we can make informed decisions, plan for the future, and embrace the ever-changing conditions of our atmosphere.
FAQ
How accurate are weather forecasts?
+The accuracy of weather forecasts depends on various factors, including the complexity of atmospheric processes, data availability, and the limitations of weather models. Short-term forecasts are generally more accurate, while long-term forecasts have a higher degree of uncertainty. Advances in technology and model development have significantly improved forecast accuracy over the years.
What are the challenges of weather prediction in tropical regions?
+Tropical regions present unique challenges due to the complex interplay of moisture, convective processes, and the formation of tropical cyclones. The rapid development and movement of these weather systems require specialized models and expertise. Meteorologists in tropical regions focus on tracking and forecasting the behavior of tropical storms and hurricanes.
How do weather forecasts impact transportation systems?
+Weather conditions can have a significant impact on transportation systems, including road, rail, and aviation. Real-time weather forecasts are crucial for ensuring the safety and efficiency of transportation networks. Severe weather warnings prompt the implementation of emergency protocols and can alter travel plans. Accurate weather predictions are particularly critical for aviation, helping pilots navigate around hazardous weather conditions.
What role do weather forecasts play in emergency management and disaster response?
+Weather forecasts are vital for emergency management and disaster response efforts. Accurate and timely weather predictions allow emergency responders to prepare and respond effectively to severe weather events such as hurricanes, floods, or wildfires. Meteorologists work closely with emergency management agencies to provide critical weather information and support decision-making during crisis situations.
How can the public contribute to improving weather prediction accuracy?
+The public can play a crucial role in improving weather prediction accuracy by providing feedback and engaging with meteorologists and weather organizations. User feedback helps meteorologists understand the needs and preferences of the community, allowing them to tailor forecasts and provide more relevant information. Additionally, reporting local weather observations can contribute to the vast network of data used in weather prediction.
