10+ Military Pay Insights: Essential Guide To 2024 Reserve Compensation
Understanding Military Reserve Compensation

The military reserve compensation system is a complex and multifaceted structure designed to provide financial support to those who serve their country while maintaining their civilian careers. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various aspects of military pay for reserves in 2024, offering valuable insights for those considering or currently serving in the reserves. By the end of this article, you will have a deeper understanding of the compensation package, its components, and how it can benefit your financial well-being.
The Basics of Military Reserve Pay
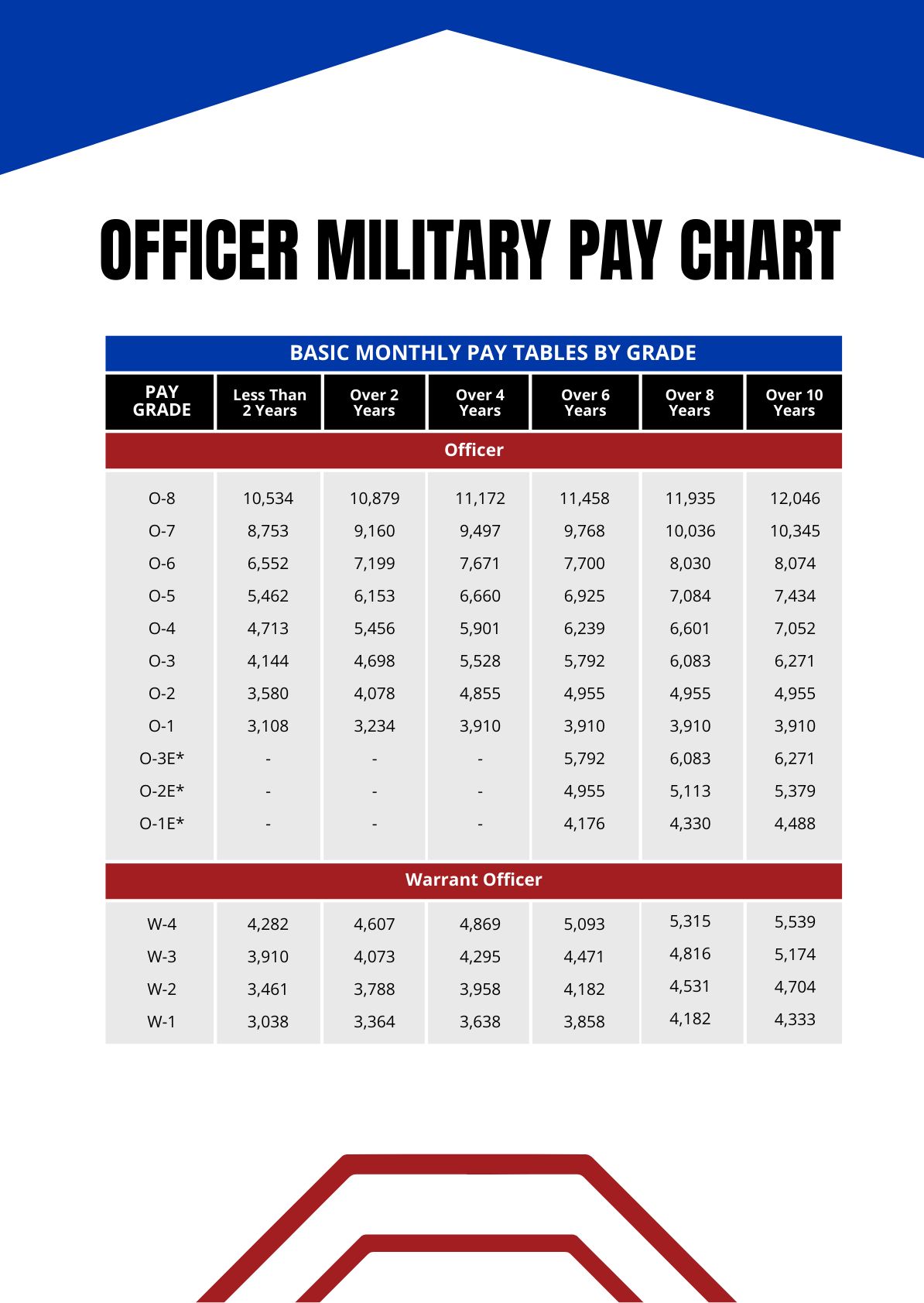
Base Pay and Rank: Military reserve pay is primarily based on two key factors: rank and time spent in service. Each rank, from the lowest to the highest, comes with a corresponding pay grade, which determines the base salary. The longer an individual serves, the higher their rank can be, leading to increased base pay.
Drill Pay: One unique aspect of reserve compensation is drill pay. Reservists typically participate in regular drills or training sessions, for which they receive additional compensation. Drill pay is calculated based on the number of drills attended and the reservist’s rank. It serves as an incentive for active participation and commitment to the reserves.
Active Duty Pay: In certain circumstances, reservists may be called to active duty, either for short-term missions or extended periods. During this time, they receive active duty pay, which is equivalent to the salary of their full-time counterparts. This ensures that reservists are fairly compensated for their contributions during active service.
Understanding Reserve Retirement Benefits
Retirement Eligibility: To be eligible for military retirement benefits, reservists must meet specific criteria. Generally, they need to have served for a minimum number of years, often 20 years, and achieved a certain rank. Retirement benefits provide a stable income source for life, offering financial security for those who have dedicated their careers to the reserves.
Pension Calculation: The retirement pension is calculated based on a reservist’s highest 36 months of base pay, multiplied by a percentage determined by their years of service. The longer an individual serves, the higher the pension amount. This pension serves as a crucial source of income during retirement, providing financial stability and peace of mind.
Healthcare Benefits: In addition to retirement pay, reservists who meet the eligibility criteria also gain access to comprehensive healthcare benefits. These benefits cover a range of medical services, ensuring that retirees have access to quality healthcare throughout their golden years.
Special Pay and Allowances
Special Pay Opportunities: Military reserves offer various special pay opportunities to incentivize specific skills or assignments. For instance, reservists with critical skills, such as pilots or medical professionals, may be eligible for additional pay. Additionally, those deployed to high-risk areas or involved in hazardous duties may receive hazard pay. These special pays recognize the unique contributions and sacrifices made by reservists.
Allowances and Incentives: To further enhance compensation, the military provides various allowances and incentives. For example, reservists may receive housing allowances, especially if they are stationed away from their primary residence. Other allowances, such as clothing or education allowances, are also available to support reservists’ needs and encourage continued service.
Tax Benefits and Savings Plans
Tax Advantages: Military reserve compensation often comes with tax advantages. Reservists may be eligible for tax deductions or credits related to their service, reducing their overall tax burden. Additionally, certain retirement savings plans, such as the Thrift Savings Plan (TSP), offer tax-deferred growth, allowing reservists to save for their future more efficiently.
Retirement Savings Plans: The military provides reservists with access to retirement savings plans, such as the TSP, which offers a range of investment options. By contributing to these plans, reservists can build a substantial retirement nest egg, taking advantage of tax-deferred growth and potential employer matching contributions.
Education Benefits
Tuition Assistance: One of the most attractive benefits of serving in the military reserves is the access to education benefits. Reservists can receive tuition assistance for pursuing higher education, allowing them to enhance their skills and knowledge while serving their country. This assistance covers a significant portion of tuition fees, making education more accessible and affordable.
GI Bill Benefits: Reservists who meet the eligibility criteria may also qualify for the Post-9⁄11 GI Bill. This benefit provides financial support for education, including tuition, fees, and a housing allowance. The GI Bill can be used for various educational pursuits, from traditional degree programs to vocational training, offering reservists the opportunity to invest in their future and pursue their career goals.
Step-by-Step Guide to Claiming Compensation
Step 1: Understand Your Eligibility: Before claiming any compensation, it is crucial to understand your eligibility. Review the criteria for base pay, drill pay, and any special pays you may be entitled to. Ensure you meet the requirements for each category to maximize your compensation.
Step 2: Calculate Your Entitlement: Utilize the official military pay charts and calculators to determine your exact compensation. These tools take into account your rank, years of service, and any applicable special pays. Accurate calculation ensures you receive the correct amount.
Step 3: Complete the Necessary Paperwork: To claim your compensation, you will need to complete and submit the appropriate forms. These forms may include drill attendance records, active duty orders, or documentation for special pays. Ensure all information is accurate and up-to-date to avoid delays in processing.
Step 4: Stay Informed About Changes: Military compensation is subject to periodic updates and adjustments. Stay informed about any changes to pay scales, allowances, or benefits. By staying updated, you can ensure you are aware of any new opportunities or adjustments that may impact your compensation.
Important Notes:
💡 Note: The information provided in this guide is based on the current military pay structure for reserves in 2024. It is essential to stay updated with any changes or modifications that may occur in the future. Regularly check official military websites or consult with military finance specialists for the most accurate and up-to-date information.
💰 Note: Military reserve compensation is subject to federal, state, and local taxes. It is advisable to consult with a tax professional to understand your specific tax obligations and maximize your tax benefits.
📝 Note: The steps outlined in the guide are general guidelines. Each reservist's situation may vary, and it is crucial to consult with military finance specialists or your chain of command for personalized advice and assistance.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, understanding the military reserve compensation system is crucial for those considering or already serving in the reserves. By grasping the basics of base pay, drill pay, and active duty pay, as well as exploring retirement benefits, special pays, and allowances, reservists can make informed decisions about their financial future. Additionally, taking advantage of tax benefits, retirement savings plans, and education opportunities further enhances the overall compensation package. Stay informed, seek professional advice when needed, and make the most of the opportunities available to ensure a secure and rewarding military career.
FAQ

What is the average military reserve pay in 2024?
+The average military reserve pay can vary based on rank and years of service. However, as of 2024, the base pay for a reservist with the rank of E-4 (Specialist/Corporal) is approximately 2,600 per month for full-time service. Drill pay for a reservist with the same rank is around 320 per drill weekend.
Are there any tax benefits for military reservists?
+Yes, military reservists may be eligible for various tax benefits. These include deductions for active duty pay, tax credits for certain military-related expenses, and potential tax-free combat pay. It is advisable to consult with a tax professional to understand your specific tax advantages.
How do I calculate my military retirement pension?
+Calculating your military retirement pension involves multiplying your highest 36 months of base pay by a percentage determined by your years of service. For example, if you have 20 years of service, your pension would be calculated as 40% of your highest 36 months of base pay. Consult official military resources for detailed pension calculation guidelines.
Can I receive both active duty pay and drill pay simultaneously?
+No, you cannot receive both active duty pay and drill pay simultaneously. Active duty pay is typically provided when reservists are called to full-time active duty, replacing their drill pay. However, you may be eligible for other special pays or allowances during active duty.
Are there any education benefits for military reservists?
+Yes, military reservists have access to a range of education benefits. These include tuition assistance, which covers a significant portion of tuition fees for higher education, and the Post-9⁄11 GI Bill, which provides financial support for education, including tuition, fees, and a housing allowance.