Design The Ultimate Security Strategy Now

Creating a robust security strategy is crucial in today's digital landscape, where threats and cyberattacks are ever-evolving. A well-designed security strategy ensures the protection of sensitive data, systems, and networks, safeguarding businesses and individuals from potential harm. In this blog post, we will delve into the key components of an ultimate security strategy, providing a comprehensive guide to enhance your organization's defense mechanisms.
Understanding the Threat Landscape
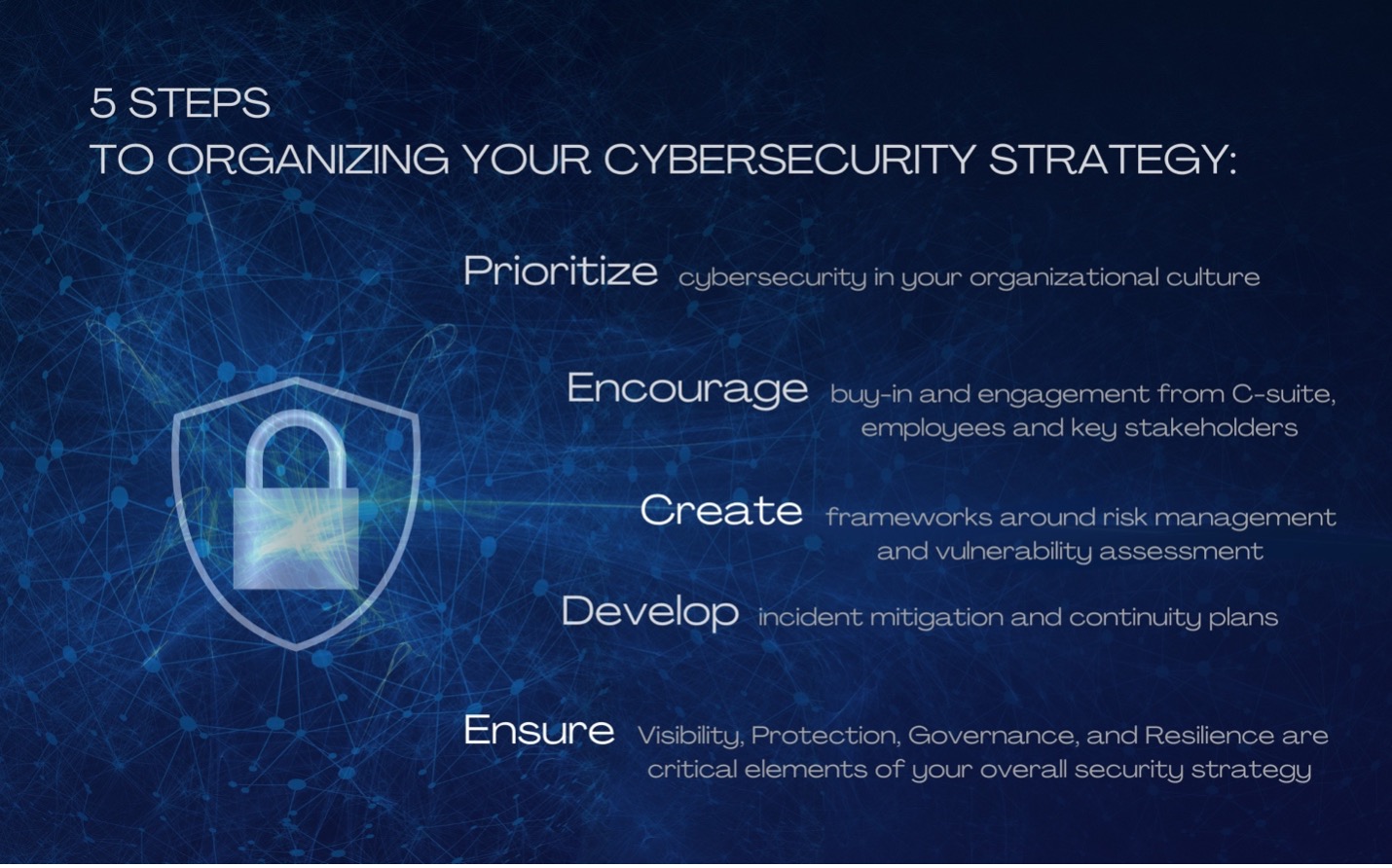
Before crafting a security strategy, it is imperative to comprehend the nature of potential threats. The threat landscape is diverse, encompassing various attack vectors and malicious actors. Common threats include:
- Malware and Ransomware: These malicious software programs can infiltrate systems, encrypt data, and demand ransom payments.
- Phishing and Social Engineering: Attackers use deceptive tactics to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information or installing malware.
- Insider Threats: Employees or contractors with authorized access can pose a risk if their intentions turn malicious.
- Zero-Day Exploits: Unpatched vulnerabilities in software or systems can be exploited by attackers before a fix is available.
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks: These attacks aim to overload networks or servers, rendering them inaccessible.
By identifying and understanding these threats, organizations can develop targeted strategies to mitigate risks effectively.
Implementing a Multi-Layered Defense

A comprehensive security strategy employs a multi-layered approach, combining various security measures to create a robust defense. Here are some essential layers to consider:
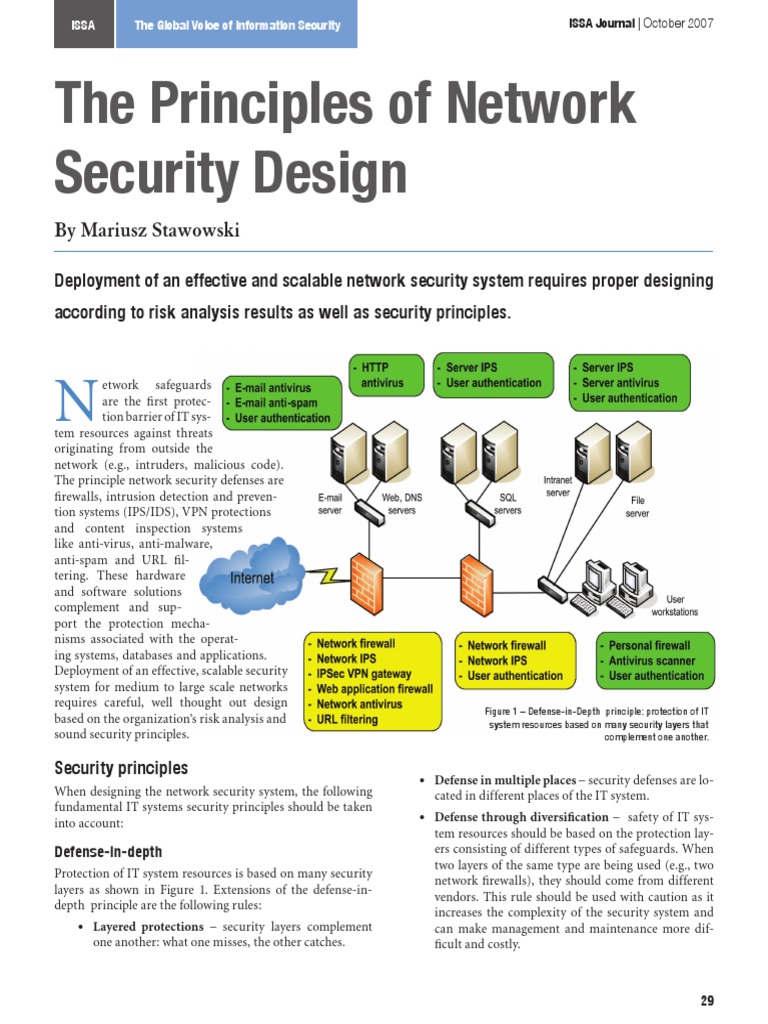
Network Security
Securing your network infrastructure is crucial to prevent unauthorized access and mitigate potential threats. Implement the following measures:
- Firewalls: Deploy firewalls to monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic, blocking potential threats.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): These systems detect and respond to suspicious activities, identifying and blocking potential attacks.
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): VPNs encrypt data transmission, ensuring secure remote access to your network.
- Network Segmentation: Divide your network into segments to limit the impact of a breach and contain potential threats.
Endpoint Protection
Endpoints, such as computers, servers, and mobile devices, are potential entry points for attackers. Protecting these endpoints is vital:
- Antivirus and Anti-Malware Software: Install reputable antivirus solutions to detect and remove malware, ensuring real-time protection.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): EDR tools provide advanced threat detection and response capabilities, analyzing endpoint activities for potential threats.
- Device Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data on endpoints to prevent unauthorized access in case of device loss or theft.
- Patch Management: Regularly update and patch software and operating systems to address known vulnerabilities.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Implementing strong IAM practices ensures that only authorized individuals have access to sensitive resources. Consider the following:
- Strong Authentication: Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of security beyond passwords.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Assign access permissions based on user roles, limiting potential damage from compromised accounts.
- Password Management: Enforce strong password policies and consider using password managers to store complex, unique passwords.
- User Activity Monitoring: Monitor user behavior to detect anomalies and potential insider threats.
Data Security
Protecting sensitive data is critical to maintaining privacy and avoiding data breaches. Implement these data security measures:
- Encryption: Encrypt data both at rest and in transit to prevent unauthorized access and data leakage.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Implement DLP solutions to monitor and control the flow of sensitive data, preventing accidental or malicious data leaks.
- Backup and Recovery: Regularly back up critical data and implement robust recovery plans to ensure business continuity in the event of a breach or data loss.
- Data Classification: Classify data based on sensitivity levels to prioritize protection efforts and implement appropriate access controls.
Security Awareness and Training

Human error is a significant factor in many security breaches. Investing in security awareness and training programs is essential to educate employees about potential threats and best practices. Here are some key elements to consider:
- Phishing Simulation: Conduct regular phishing simulations to test employees' ability to identify and report suspicious emails.
- Security Training Sessions: Organize training sessions to educate employees about common security threats, safe browsing practices, and password hygiene.
- Incident Reporting: Establish clear procedures for reporting security incidents, ensuring prompt response and mitigation.
- Regular Updates: Keep employees informed about emerging threats and provide ongoing security awareness training to reinforce best practices.
Incident Response Planning

Despite our best efforts, security incidents can still occur. Having a well-defined incident response plan is crucial to minimize the impact and swiftly recover from an attack. Key components of an effective incident response plan include:
- Incident Response Team: Establish a dedicated team with defined roles and responsibilities to manage and respond to security incidents.
- Incident Response Procedures: Document clear procedures for identifying, containing, eradicating, and recovering from security incidents.
- Forensic Analysis: Conduct thorough forensic investigations to determine the root cause of an incident and gather evidence for legal or insurance purposes.
- Business Continuity Planning: Develop plans to ensure business operations can continue during and after a security incident, minimizing downtime and financial losses.
Continuous Monitoring and Improvement

Security is an ongoing process, and continuous monitoring is essential to stay ahead of evolving threats. Implement the following practices:
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Utilize SIEM solutions to collect, analyze, and correlate security-related data from various sources, providing real-time visibility into potential threats.
- Threat Intelligence: Stay updated with the latest threat intelligence to identify emerging attack patterns and potential vulnerabilities.
- Penetration Testing: Conduct regular penetration tests to identify and address vulnerabilities in your systems and networks.
- Security Audits: Perform periodic security audits to assess the effectiveness of your security controls and identify areas for improvement.
Collaborative Security

Security is a shared responsibility, and collaboration is key to strengthening your defense. Consider the following collaborative approaches:
- Partnering with Security Experts: Engage with security experts or managed security service providers to benefit from their expertise and specialized skills.
- Information Sharing: Participate in information-sharing platforms and communities to stay updated on the latest threats and best practices.
- Industry Collaboration: Collaborate with industry peers to share insights, learn from each other's experiences, and collectively enhance security measures.
- Government and Law Enforcement: Establish relationships with relevant government agencies and law enforcement to report incidents and seek assistance when needed.
By adopting a collaborative approach, you can leverage the collective knowledge and resources of the security community to strengthen your security posture.
Conclusion
Designing the ultimate security strategy requires a holistic approach, addressing various aspects of cybersecurity. By understanding the threat landscape, implementing a multi-layered defense, investing in security awareness, and planning for incident response, organizations can significantly enhance their security posture. Continuous monitoring, improvement, and collaboration are essential to stay ahead of evolving threats and protect sensitive data and systems.
What are some common challenges in implementing a security strategy?
+Common challenges include budget constraints, lack of skilled personnel, and keeping up with the rapidly evolving threat landscape. It’s important to prioritize security investments and continuously educate employees to overcome these challenges.
How often should security awareness training be conducted?
+Security awareness training should be conducted regularly, ideally on a quarterly or semi-annual basis. However, additional training sessions may be required in response to specific threats or incidents.
What are some best practices for incident response planning?
+Best practices include establishing a dedicated incident response team, conducting regular tabletop exercises to simulate incidents, and regularly reviewing and updating incident response procedures.
How can I stay updated with the latest threat intelligence?
+Stay connected with security communities, subscribe to reputable security blogs and newsletters, and participate in industry conferences and events to access the latest threat intelligence and best practices.