Israel, Hezbollah & Lebanon: A Comprehensive Guide To The Conflict
The complex and protracted conflict between Israel, Hezbollah, and Lebanon has spanned decades, shaping the political landscape of the Middle East. This comprehensive guide aims to unravel the historical context, key players, and ongoing tensions that define this enduring dispute.
Historical Context

The roots of the Israel-Hezbollah-Lebanon conflict can be traced back to the establishment of the State of Israel in 1948. Lebanon, as a neighboring country, has been directly impacted by the Israeli-Palestinian conflict and the subsequent regional tensions.
The Lebanese Civil War (1975-1990) further complicated matters, creating a power vacuum that allowed various factions, including Hezbollah, to gain influence. Hezbollah, an Islamic political and military organization, emerged as a significant force in the early 1980s, primarily focused on resisting Israeli occupation in southern Lebanon.
Key Players and Their Roles

Israel
Israel, a sovereign state in the Middle East, has been involved in various conflicts with its neighbors since its inception. The Israeli government considers Hezbollah a significant threat due to its military capabilities and its support for Palestinian resistance movements.
Hezbollah
Hezbollah, also known as the Party of God, is a Shiite Islamic organization with a dual political and military structure. Founded in 1982, it has evolved from a resistance group to a political party with representation in the Lebanese government.
Hezbollah's military wing is well-equipped and trained, posing a challenge to Israeli security. The organization's primary objectives include the liberation of Lebanese territories under Israeli control and support for Palestinian self-determination.
Lebanon
Lebanon, officially the Lebanese Republic, is a small country with a diverse population. The Lebanese government has often struggled to maintain control over its territory, particularly in the face of Israeli incursions and Hezbollah's growing influence.
Lebanon's position as a neighbor to both Israel and Syria has made it a key player in regional politics. The country's fragile political balance and its role as a host to Palestinian refugee camps have further complicated its relationship with Israel and Hezbollah.
Major Events and Conflicts

The South Lebanon Conflict (1982-2000)
The South Lebanon conflict, also known as the War of Attrition, began with Israel's invasion of Lebanon in 1982. This invasion aimed to weaken the Palestinian Liberation Organization (PLO) and prevent attacks on northern Israel. However, it also led to the rise of Hezbollah as a significant resistance force.
During this period, Israel occupied a "security zone" in southern Lebanon, engaging in frequent clashes with Hezbollah fighters. The conflict resulted in the deaths of thousands of civilians and the displacement of many more.
The 2006 Lebanon War
The 2006 Lebanon War, also known as the Second Lebanon War, was a 34-day conflict between Israel and Hezbollah. It began with a cross-border raid by Hezbollah, resulting in the capture of two Israeli soldiers and the killing of eight others. Israel responded with a massive military operation, targeting Hezbollah's infrastructure and launching air strikes across Lebanon.
The war caused extensive damage to Lebanese infrastructure and resulted in the displacement of over one million Lebanese civilians. It also led to the deaths of over 1,000 Lebanese civilians and approximately 160 Israelis, including soldiers and civilians.
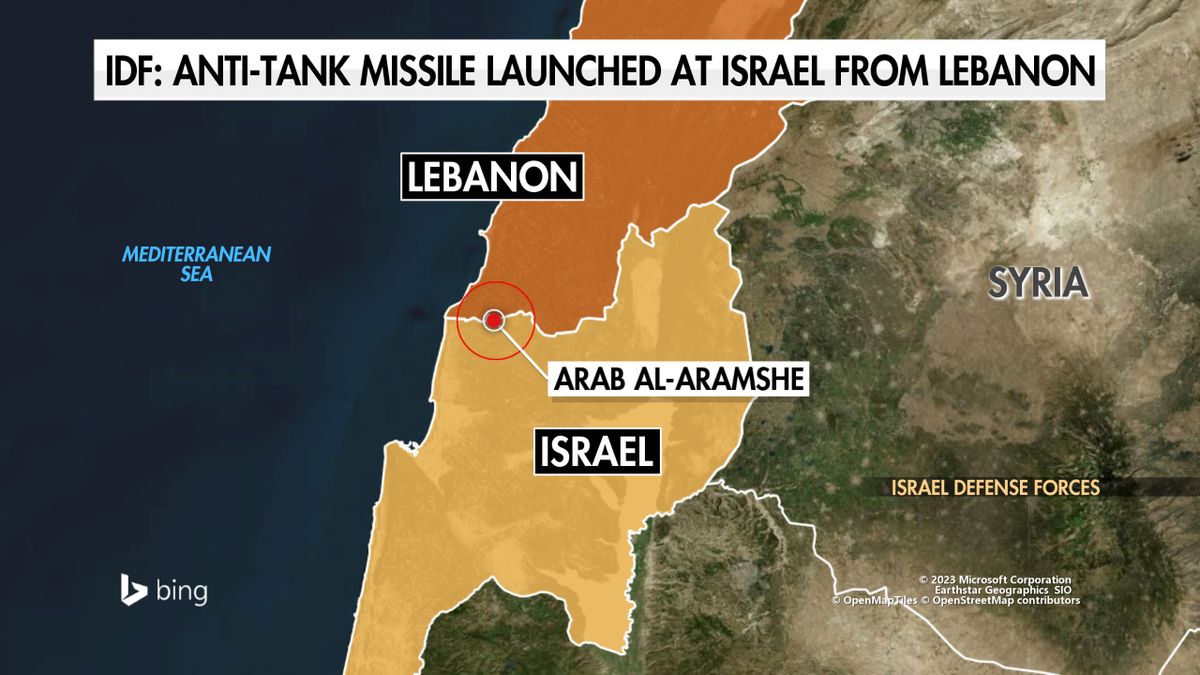
Ongoing Tensions and Border Clashes
Despite several ceasefires and attempts at peace, tensions between Israel and Hezbollah have persisted. Border clashes, exchanges of fire, and occasional incursions have continued to occur, keeping the region in a state of heightened alert.
Hezbollah's increasing military capabilities, including its arsenal of rockets and missiles, have been a significant concern for Israel. The organization's involvement in the Syrian Civil War and its support for the Assad regime have further complicated the regional dynamics.
International Involvement and Peace Efforts

The international community, particularly the United Nations (UN), has played a crucial role in mediating and facilitating peace efforts between Israel, Hezbollah, and Lebanon.
United Nations Interim Force in Lebanon (UNIFIL)
The UNIFIL was established in 1978 to oversee the withdrawal of Israeli forces from southern Lebanon. Its mandate has been extended and modified over the years to maintain peace and stability along the Israel-Lebanon border.
UNIFIL's presence has been instrumental in preventing major conflicts and facilitating negotiations between the parties. However, its effectiveness has been challenged by ongoing tensions and the complex political landscape.
Peace Talks and Agreements
Various peace talks and agreements have been attempted over the years to resolve the Israel-Hezbollah-Lebanon conflict. The 1983 Israel-Lebanon Agreement, for example, aimed to withdraw Israeli forces from Lebanon. However, it ultimately failed due to opposition from various Lebanese factions.
More recently, the 2002 Arab Peace Initiative proposed a comprehensive peace plan for the Middle East, including the normalization of relations between Israel and Arab states. While it received support from some Arab countries, it has yet to be fully implemented.
Humanitarian Impact and Refugee Crisis

The ongoing conflict has had a devastating humanitarian impact on the people of Lebanon and the region. The displacement of civilians, destruction of infrastructure, and the loss of lives have created a complex refugee crisis.
Lebanon, with its limited resources, has struggled to accommodate the large number of refugees, including those from Syria. The economic and social strain has further exacerbated the country's political instability.
International organizations and aid agencies have played a vital role in providing humanitarian assistance to those affected by the conflict. However, the scale of the crisis continues to pose significant challenges.
Notes

🌟 Note: This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the Israel-Hezbollah-Lebanon conflict. While it covers the key aspects, the complexity of the situation may require further exploration and research.
⚠️ Note: The information presented here is based on available data and sources. For the most up-to-date and accurate information, it is recommended to refer to official government websites and reputable news outlets.
Conclusion

The Israel-Hezbollah-Lebanon conflict is a complex and multifaceted issue, rooted in historical tensions and regional dynamics. The ongoing struggles between these parties have had profound implications for the people of the region, leading to loss of life, displacement, and political instability.
Despite various attempts at peace and international mediation, the conflict persists, with border clashes and military build-up posing a constant threat. The involvement of external powers and the regional power struggle further complicate the prospects for a lasting resolution.
As the conflict continues to evolve, it is essential for all parties involved to prioritize diplomacy and peaceful negotiations. The humanitarian impact and the potential for further escalation highlight the urgency of finding a sustainable solution that addresses the underlying causes of the conflict.
FAQ

What is the primary objective of Hezbollah in the conflict with Israel?
+Hezbollah’s primary objective is to resist Israeli occupation and support Palestinian self-determination. The organization seeks to liberate Lebanese territories under Israeli control and protect Lebanon’s sovereignty.
How has the Syrian Civil War impacted the Israel-Hezbollah-Lebanon conflict?
+The Syrian Civil War has complicated the regional dynamics, with Hezbollah actively supporting the Assad regime. This involvement has drawn Israel’s attention and led to increased tensions along the Israel-Lebanon border.
What role does the United Nations play in mediating the conflict?
+The United Nations, through the UNIFIL, plays a crucial role in maintaining peace and stability along the Israel-Lebanon border. The UN also facilitates peace talks and agreements, aiming to find a diplomatic solution to the conflict.
How has the refugee crisis affected Lebanon’s stability?
+The refugee crisis, including the influx of Syrian refugees, has placed a significant strain on Lebanon’s resources and infrastructure. This has contributed to political instability and economic challenges within the country.
What are the prospects for a peaceful resolution to the conflict?
+The prospects for a peaceful resolution remain challenging due to the complex nature of the conflict and the involvement of multiple parties. However, ongoing diplomatic efforts and international mediation provide a glimmer of hope for a sustainable solution.