Military Hourly Pay Rate
Understanding the military hourly pay rate is essential for anyone considering a career in the armed forces. This comprehensive guide will delve into the various aspects of military compensation, including the factors that influence hourly rates, the different pay grades, and the benefits and allowances that come with military service. By the end of this article, you'll have a clear understanding of how military pay works and what to expect financially.
Factors Affecting Military Hourly Pay

The military hourly pay rate is not a one-size-fits-all system. Several factors contribute to the calculation of an individual's pay, ensuring that compensation is fair and reflective of the unique skills and responsibilities associated with each role.
Pay Grade and Rank
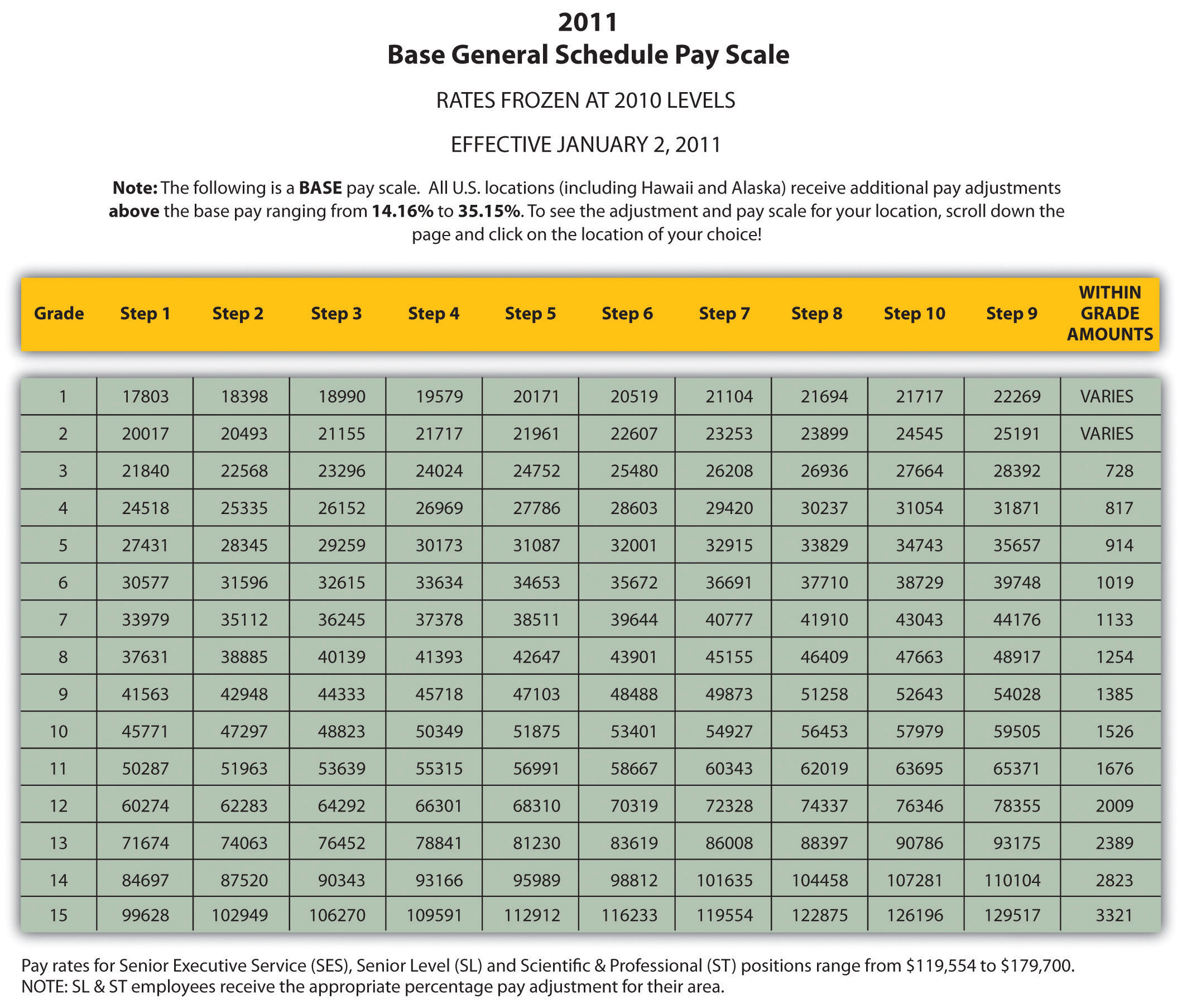
The military uses a structured pay grade system, often referred to as pay grades or ranks. These grades determine the base pay for service members. There are typically several pay grades within each branch of the military, ranging from entry-level to the highest ranks.
| Pay Grade | Description |
|---|---|
| E-1 to E-3 | Entry-level ranks for enlisted personnel. |
| E-4 to E-6 | Mid-level ranks, often with increased responsibilities. |
| E-7 to E-9 | Senior enlisted ranks, known for leadership roles. |
| O-1 to O-10 | Officer ranks, starting with junior officers and progressing to the highest military ranks. |

Years of Service
The longer an individual serves in the military, the higher their pay is likely to be. Years of service are a significant factor in determining hourly rates, as they reflect experience, loyalty, and dedication to the armed forces.
Specialty and Skills
Military pay rates also consider the specific skills and specialties of service members. Certain roles, such as pilots, engineers, or specialized technicians, often command higher pay due to the unique and critical nature of their jobs.
Location and Deployment
The geographic location of a service member's duty station can impact their pay. Additionally, deployment to high-risk or remote areas may result in additional allowances or incentives to compensate for the unique challenges and dangers associated with these assignments.
Calculating Military Hourly Pay

Military hourly pay is calculated based on a combination of the factors mentioned above. The process involves determining the base pay rate for the individual's pay grade and then adjusting it based on years of service, specialty, and any applicable allowances or incentives.
Base Pay Rates
Each pay grade has a corresponding base pay rate, which is determined by the military's pay tables. These rates are updated annually to account for cost-of-living adjustments and other economic factors. The base pay provides a starting point for calculating an individual's total compensation.
Adjustments and Allowances
- Years of Service: Service members receive incremental pay increases for each year of service, with higher rates for longer tenures.
- Specialty Pay: Certain military occupations, such as medical professionals or linguists, may receive additional pay based on their unique skills.
- Deployment Pay: Service members deployed to hazardous or remote areas may be eligible for special pay, known as imminent danger pay or hardship duty pay.
- Family Separation Allowance: This allowance compensates service members for extended periods away from their families due to deployment or other military assignments.
Understanding Military Benefits
In addition to hourly pay, military service comes with a comprehensive package of benefits and allowances that enhance the overall compensation package. These benefits are designed to support service members and their families, providing stability and security during and after their military careers.
Health and Dental Care
The military provides comprehensive health and dental care to active-duty service members and their dependents. This includes access to military hospitals, clinics, and dental facilities, ensuring that individuals receive high-quality medical services at little to no cost.
Housing and Subsidies
- Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH): Service members who do not live in military housing receive a BAH to cover the costs of rent or mortgage payments.
- Military Housing: Many military bases offer on-base housing, providing service members and their families with a stable and secure living environment.
Education and Training Opportunities
The military places a strong emphasis on education and professional development. Service members have access to various training programs, courses, and certifications to enhance their skills and knowledge. Additionally, the GI Bill provides financial support for education and training after military service.
Retirement and Pension Plans
Military service members are eligible for generous retirement and pension plans. After completing a certain number of years of service, individuals can retire with a guaranteed pension, ensuring financial stability in their post-military lives.
Other Benefits
- Commissary and Exchange Privileges: Service members can shop at military commissaries and exchanges, offering discounted prices on groceries, clothing, and other goods.
- Travel and Transportation Benefits: The military provides various travel and transportation benefits, including discounted airfare and access to military transportation systems.
- Life Insurance: Service members are automatically enrolled in the Servicemembers' Group Life Insurance (SGLI) program, providing financial protection for their families in case of death or disability.
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating Your Military Pay

Calculating your military pay involves a series of steps to ensure accuracy. Here's a simplified guide to help you estimate your hourly rate:
-
Determine Your Pay Grade: Identify your current pay grade or rank within the military. This information can be found on your pay stub or through official military resources.
-
Find the Base Pay Rate: Look up the base pay rate corresponding to your pay grade using the military's pay tables. These tables are updated annually and can be accessed online.
-
Calculate Years of Service Pay: Multiply your base pay rate by your years of service to determine the additional pay you receive for your tenure in the military.
-
Consider Specialty Pay: If you have a specialized skill or occupation, research the additional pay associated with your role. This information is typically available through military resources or your chain of command.
-
Add Deployment and Allowances: If you are currently deployed or eligible for special allowances, calculate these additional payments based on the specific rates and guidelines provided by the military.
-
Total Compensation: Sum up all the components calculated in the previous steps to arrive at your estimated total military pay.
🌟 Note: Remember that this guide provides a simplified overview of military pay calculation. For precise and up-to-date information, refer to official military resources or consult with your unit's finance office.
Military Pay Grades and Ranks

The military pay grade system is a structured hierarchy that defines the ranks and responsibilities of service members. Understanding the pay grades can help individuals navigate their military careers and plan for future opportunities.
Enlisted Pay Grades (E-1 to E-9)
Enlisted personnel make up the majority of the military workforce. They are responsible for carrying out various operational and support tasks. The enlisted pay grades range from E-1 to E-9, with each grade representing a different level of experience and responsibility.
Officer Pay Grades (O-1 to O-10)
Officers are leaders within the military, responsible for making strategic decisions and overseeing operations. The officer pay grades, ranging from O-1 to O-10, reflect the increasing levels of authority and responsibility associated with these roles.
Warrant Officer Pay Grades (W-1 to W-5)
Warrant officers are highly skilled specialists who provide technical expertise and leadership in specific military fields. The warrant officer pay grades, W-1 to W-5, recognize their unique skills and contributions to the armed forces.
The Future of Military Pay
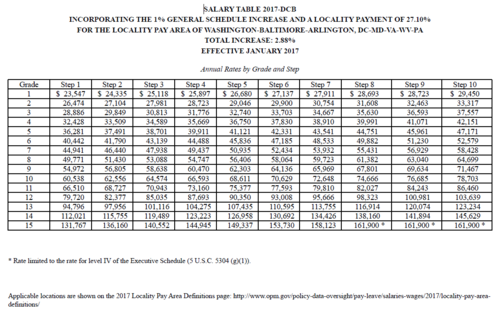
The military pay system is subject to ongoing evaluation and adjustments to ensure it remains fair, competitive, and attractive to potential recruits. Here are some key considerations for the future of military pay:
- Cost-of-Living Adjustments: The military regularly reviews and adjusts pay rates to account for changes in the cost of living, ensuring that service members' compensation keeps pace with inflation.
- Market Equitable Pay: The military aims to maintain competitive pay rates compared to civilian occupations with similar skill sets and responsibilities.
- Recruitment and Retention: Military pay and benefits play a crucial role in attracting and retaining talented individuals. The armed forces continually assess their compensation packages to ensure they remain competitive in the job market.
- Advancements in Technology: As military technology advances, new specialties and skills may emerge, requiring adjustments to pay rates to reflect the increased value of these roles.
FAQs

What is the difference between pay grade and rank in the military?
+Pay grade refers to the specific level of pay an individual receives based on their rank and years of service. Rank, on the other hand, represents the position of authority and responsibility within the military hierarchy.
Are there any tax benefits for military personnel?
+Yes, military personnel may be eligible for certain tax benefits, such as the exclusion of basic housing allowance from taxable income. It's important to consult with a tax professional to understand the specific benefits available to you.
Can military pay be garnished for child support or other debts?
+Military pay can be garnished for child support obligations, but there are limits to how much can be deducted. For other types of debts, the process is more complex and may require legal intervention.
Are there any special pay incentives for specific military occupations?
+Yes, certain military occupations, such as pilots, cyber security specialists, and medical professionals, may be eligible for special pay incentives. These incentives are designed to attract and retain individuals with unique skills and expertise.
How often are military pay rates adjusted?
+Military pay rates are typically adjusted annually to account for cost-of-living changes and other economic factors. These adjustments are announced and implemented by the military leadership.
Conclusion

Understanding the military hourly pay rate is crucial for anyone considering a career in the armed forces. The military’s structured pay system considers various factors, including pay grade, rank, years of service, specialty, and deployment. Additionally, military service comes with a comprehensive package of benefits and allowances that enhance overall compensation. By exploring the factors that influence military pay and the resources available to calculate and understand your compensation, you can make informed decisions about your military career and financial future.