Military Ranks Us Army

The United States Army is renowned for its well-structured and hierarchical system of military ranks. These ranks not only define an individual's position and responsibilities within the military but also play a crucial role in maintaining discipline and order. Understanding the US Army's rank structure is essential for anyone interested in military history, current affairs, or even those considering a career in the armed forces. In this blog post, we will delve into the intricate world of military ranks in the US Army, exploring the various levels, their significance, and the paths to promotion.
Enlisted Ranks
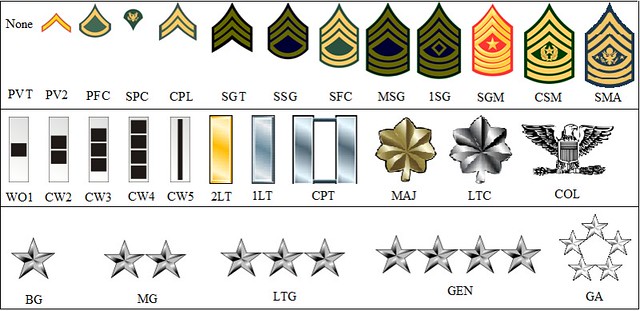
The enlisted ranks form the backbone of the US Army, comprising the majority of its personnel. These ranks are often referred to as the "Non-Commissioned Officers" (NCOs) and are responsible for carrying out the day-to-day operations and providing essential support to the higher-ranking officers.
Private (E-1) and Private (E-2)
Private is the lowest enlisted rank in the US Army. Privates are typically new recruits who are still in the process of completing their basic training. They are often referred to as "privates first class" (PFCs) and are still learning the ropes of military life.
Private First Class (E-3)
After completing basic training, soldiers are promoted to Private First Class. This rank signifies a higher level of proficiency and responsibility. PFCs are often assigned more complex tasks and are expected to demonstrate leadership skills.
Specialist (E-4)
The rank of Specialist is unique to the US Army and is awarded to soldiers who have demonstrated exceptional skills and expertise in their respective fields. Specialists are often subject matter experts and play a vital role in supporting the mission.
Corporal (E-4)
Corporals are the first level of NCOs and are responsible for leading small teams or squads. They are tasked with training and mentoring junior soldiers, ensuring discipline, and providing on-the-ground leadership during operations.
Sergeant (E-5)
Sergeants are senior NCOs who serve as squad leaders or platoon sergeants. They are responsible for the overall performance and discipline of their squads, ensuring that orders are carried out effectively. Sergeants are often highly respected for their experience and leadership abilities.
Staff Sergeant (E-6)
Staff Sergeants are key leaders within the US Army. They serve as platoon sergeants or section chiefs, providing guidance and supervision to multiple squads. Staff Sergeants are known for their expertise and are often sought out for their knowledge and experience.
Sergeant First Class (E-7)
Sergeant First Class is a highly respected rank in the US Army. These NCOs serve as senior platoon sergeants or squad leaders and are responsible for the overall training and welfare of their troops. They are considered master soldiers and are instrumental in shaping the future leaders of the Army.
Master Sergeant (E-8)
Master Sergeants are the top-level NCOs in the US Army. They serve as company first sergeants or senior enlisted advisors to commanders. Master Sergeants are experts in their fields and play a crucial role in developing and implementing policies and procedures.
First Sergeant (E-8)
First Sergeants are unique to the US Army and hold a position of great responsibility. They serve as the senior enlisted advisor to battalion commanders and are responsible for the overall morale, discipline, and welfare of the soldiers in their battalion.
Officer Ranks

Officer ranks in the US Army are earned through a combination of education, training, and experience. These officers are responsible for making strategic decisions, leading troops, and ensuring the smooth functioning of military operations.
Second Lieutenant (O-1)
Second Lieutenants are the entry-level officers in the US Army. They are typically recent graduates of military academies or ROTC programs and are still in the process of learning the ropes of command and leadership.
First Lieutenant (O-2)
First Lieutenants are more experienced officers who have gained valuable field experience. They often serve as platoon leaders or company executives, providing guidance and direction to their subordinates.
Captain (O-3)
Captains are the first level of field-grade officers in the US Army. They are responsible for leading companies or batteries and are often considered the backbone of the officer corps. Captains are known for their decision-making skills and ability to inspire their troops.
Major (O-4)
Majors are senior field-grade officers who serve as battalion executives or company commanders. They are responsible for the overall planning and execution of operations at the battalion level. Majors are respected for their strategic thinking and leadership abilities.
Lieutenant Colonel (O-5)
Lieutenant Colonels are the first level of general officers in the US Army. They serve as battalion commanders or staff officers at higher levels. Lieutenant Colonels are key decision-makers and are responsible for the success of their units.
Colonel (O-6)
Colonels are highly experienced officers who serve as regiment or brigade commanders. They are responsible for the overall performance and readiness of their units and are often considered the backbone of the Army's leadership.
Brigadier General (O-7)
Brigadier Generals are the first level of general officers with a star. They serve as division commanders or deputy commanders at higher levels. Brigadier Generals are responsible for the strategic direction and management of large units.
Major General (O-8)
Major Generals are senior general officers who serve as corps or division commanders. They are responsible for the overall command and control of multiple brigades and are key players in the Army's leadership hierarchy.
Lieutenant General (O-9)
Lieutenant Generals are three-star generals who hold positions of great responsibility. They serve as commanders of large-scale operations or as the Army's deputy chiefs of staff. Lieutenant Generals are known for their strategic vision and ability to lead complex missions.
General (O-10)
Generals are the highest-ranking officers in the US Army. They serve as the Army's Chief of Staff or hold positions of national importance. Generals are responsible for the overall direction and policy-making of the Army and are considered the pinnacle of military leadership.
Warrant Officer Ranks

Warrant Officers in the US Army are highly skilled and specialized experts in their respective fields. They are appointed by the Secretary of the Army and are not promoted through the enlisted or officer ranks. Warrant Officers provide technical expertise and leadership in specific areas of military operations.
Warrant Officer 1 (WO1)
Warrant Officer 1 is the entry-level rank for Warrant Officers. They are selected based on their expertise and are responsible for providing technical guidance and mentoring to junior soldiers.
Chief Warrant Officer 2 (CW2)
Chief Warrant Officer 2 is the second level of Warrant Officer rank. CW2s are highly skilled specialists who serve as flight officers, maintenance officers, or in other technical roles.
Chief Warrant Officer 3 (CW3)
Chief Warrant Officer 3 is a senior Warrant Officer rank. CW3s are often team leaders or instructors, sharing their expertise with junior soldiers and ensuring the smooth functioning of specialized operations.
Chief Warrant Officer 4 (CW4)
Chief Warrant Officer 4 is the highest level of Warrant Officer rank. CW4s are master specialists and serve as senior advisors to commanders. They are instrumental in developing and implementing specialized procedures.
Chief Warrant Officer 5 (CW5)
Chief Warrant Officer 5 is the pinnacle of the Warrant Officer ranks. CW5s are the most senior technical experts and are responsible for providing strategic guidance and mentorship to the entire Warrant Officer corps.
Paths to Promotion

Promotion in the US Army is a highly competitive process, and soldiers must meet specific criteria to advance to higher ranks. Here are some key factors that contribute to promotion:
- Performance and Skills: Soldiers who consistently demonstrate exceptional performance, leadership skills, and expertise in their field are more likely to be considered for promotion.
- Education and Training: Completing advanced military education programs, such as the US Army Command and General Staff College, can enhance an individual's chances of promotion.
- Experience: Years of service and field experience play a crucial role in promotion. Soldiers with a proven track record of success and dedication are often favored.
- Leadership Potential: The US Army values leadership qualities and seeks individuals who can inspire and guide their subordinates effectively.
- Recommendations: Recommendations from superior officers and commanders carry significant weight in the promotion process.
Conclusion

The US Army's rank structure is a complex and well-defined system that reflects the hierarchy and responsibilities within the military. From the lowest enlisted ranks to the highest generals, each rank plays a vital role in maintaining the efficiency and effectiveness of the Army. Understanding this rank structure provides insight into the organization and leadership of one of the world's most respected military forces. Whether you are a history enthusiast, a military professional, or simply curious about the inner workings of the US Army, exploring the ranks and their significance offers a fascinating glimpse into the world of military service.
What is the highest rank in the US Army?
+The highest rank in the US Army is General (O-10), also known as a four-star general. This rank is held by the Army’s Chief of Staff and is considered the pinnacle of military leadership.
How long does it take to reach the rank of Sergeant in the US Army?
+The time it takes to reach the rank of Sergeant can vary depending on several factors, including performance, education, and the needs of the Army. On average, it takes approximately 3 to 4 years of service to achieve the rank of Sergeant.
Can enlisted soldiers become officers in the US Army?
+Yes, enlisted soldiers can transition to the officer ranks through various programs such as the Green to Gold program or the Warrant Officer program. These programs allow soldiers to pursue a commission and become officers in the US Army.
What is the role of Warrant Officers in the US Army?
+Warrant Officers in the US Army are highly skilled specialists who provide technical expertise and leadership in specific areas of military operations. They serve as mentors and advisors to junior soldiers and play a crucial role in specialized operations.
Are there any female generals in the US Army?
+Yes, there have been several female generals in the US Army. The first female general was Anna Mae Hays, who was promoted to Brigadier General in 1970. Since then, many women have achieved general officer ranks, breaking barriers and leading the way for future generations.
