Ultimate Guide To Emt: 7 Pro Tips

Introduction to Emergency Medical Technician (EMT) Training and Certification
Are you considering a career as an Emergency Medical Technician (EMT)? If so, you’ve come to the right place! This comprehensive guide will provide you with all the information you need to embark on this noble and challenging profession. Becoming an EMT is an incredible journey, and we’re here to equip you with the knowledge and insights to make informed decisions.
EMTs are vital members of the healthcare team, providing immediate care and transportation to individuals facing medical emergencies. Their quick thinking, expertise, and compassion can make a life-altering difference. In this guide, we’ll explore the steps to becoming an EMT, the skills you’ll need, and the rewarding career path that awaits you. So, let’s dive in!
Step 1: Understanding the Role of an EMT
Before embarking on your EMT journey, it’s crucial to grasp the responsibilities and daily life of an EMT. Here’s an overview:
- Emergency Response: EMTs are often the first responders on the scene of an emergency, whether it’s a car accident, a heart attack, or a natural disaster.
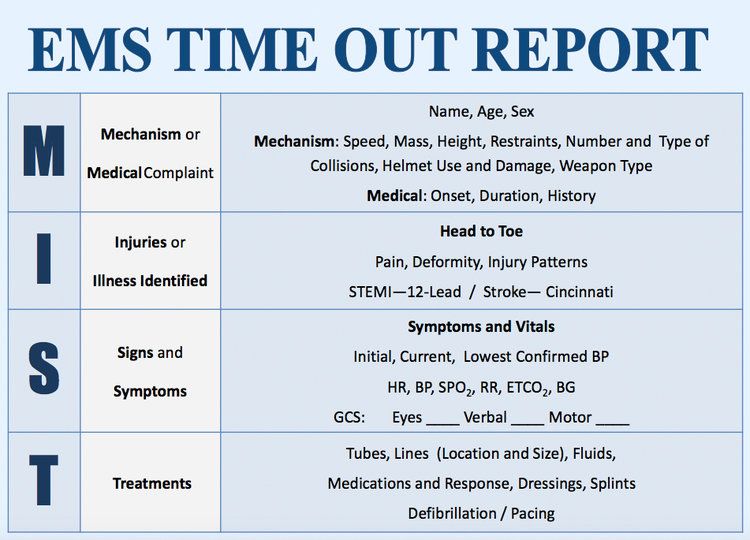
- Patient Assessment: They quickly assess the patient’s condition, identify life-threatening issues, and provide initial treatment.
- Medical Care: EMTs are trained to perform a range of medical procedures, including CPR, defibrillation, and administering oxygen.
- Transportation: Their role also involves safely transporting patients to the nearest medical facility for further treatment.
- Communication: Effective communication is key. EMTs must relay critical information to healthcare professionals at the hospital.
- Compassion: EMTs provide emotional support to patients and their families during stressful situations.
Step 2: Educational Requirements

To become an EMT, you’ll need to meet certain educational prerequisites:
- High School Diploma or Equivalent: A high school education is typically the minimum requirement. Focus on science and math courses to build a strong foundation.
- EMT Training Program: Enroll in an accredited EMT training program. These programs are offered by community colleges, technical schools, and emergency services departments.
- Program Duration: EMT training programs usually range from a few weeks to several months, depending on the level of certification you pursue.
- Curriculum: The curriculum covers a wide range of topics, including anatomy, physiology, patient assessment, emergency medical procedures, and legal aspects of healthcare.
Step 3: Choosing the Right EMT Training Program
With numerous EMT training programs available, selecting the right one is essential. Consider the following factors:
- Accreditation: Ensure the program is accredited by a recognized accrediting body, such as the Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs (CAAHEP).
- Curriculum: Review the program’s curriculum to ensure it covers all the necessary topics and meets national standards.
- Instructors: Look for programs with experienced and qualified instructors who have real-world experience as EMTs.
- Hands-on Training: Choose a program that offers ample practical training and simulation exercises to prepare you for real-life scenarios.
- Flexibility: Consider your schedule and opt for a program that offers flexible timing or online options if needed.
Step 4: EMT Certification Levels

There are different levels of EMT certification, each with its own scope of practice and responsibilities:
- EMT-Basic (EMT-B): This is the entry-level certification, covering basic life support and patient assessment skills.
- EMT-Intermediate (EMT-I): EMT-I certification builds upon EMT-B skills and includes advanced airway management and medication administration.
- EMT-Paramedic (EMT-P): Paramedics are highly skilled and can provide advanced life support, including intravenous therapy and interpreting electrocardiograms (ECGs).
Step 5: EMT Training Curriculum

The EMT training curriculum is comprehensive and covers a wide range of topics. Here’s a glimpse:
- Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the human body’s structure and function is essential for effective patient care.
- Patient Assessment: Learn to quickly assess a patient’s condition, identify critical issues, and prioritize treatment.
- Cardiac Emergencies: Gain expertise in recognizing and managing cardiac arrests, heart attacks, and other cardiovascular emergencies.
- Respiratory Emergencies: Develop skills to handle respiratory distress, asthma attacks, and other breathing-related issues.
- Trauma Management: Acquire the knowledge and techniques to manage trauma cases, including fractures, burns, and wounds.
- Medical Emergencies: Learn to handle various medical emergencies, such as diabetic emergencies, seizures, and allergic reactions.
- Pharmacology: Understand the basics of medication administration and the use of common emergency drugs.
- Legal and Ethical Considerations: Explore the legal and ethical aspects of healthcare, including patient confidentiality and informed consent.
Step 6: Hands-on Training and Clinical Rotations

Hands-on training and clinical rotations are integral parts of your EMT education. These experiences will:
- Practical Skills: Allow you to apply your theoretical knowledge in real-world scenarios.
- Confidence Building: Help you gain confidence in your abilities and decision-making skills.
- Clinical Rotations: Provide opportunities to work alongside experienced EMTs and paramedics in various healthcare settings, such as ambulance services, hospitals, and emergency departments.
Step 7: EMT Certification and Recertification
Once you’ve completed your EMT training, it’s time to obtain your certification:
- National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians (NREMT): The NREMT offers certification exams for EMTs at different levels.
- Exam Preparation: Prepare for the exams by reviewing comprehensive study materials and practice questions.
- Recertification: EMT certification typically needs to be renewed every 2-3 years. Recertification requires completing continuing education courses and maintaining a certain level of work experience.
Conclusion

Congratulations! You’ve reached the end of this comprehensive guide to becoming an Emergency Medical Technician. We hope this journey has inspired and equipped you with the knowledge to pursue this noble profession. Remember, being an EMT is not just a job; it’s a calling to make a difference in people’s lives during their most vulnerable moments.
As you embark on your EMT career, keep learning, stay dedicated, and always prioritize patient care. Your skills and compassion will make a lasting impact on the lives of those you serve. Best of luck on your EMT journey!
FAQ
What is the average salary for an EMT?
+The salary for an EMT can vary depending on factors such as location, experience, and employer. On average, EMTs earn between 30,000 and 50,000 annually. However, with additional certifications and specialized skills, EMTs can earn higher salaries.
Can I work as an EMT part-time or on a flexible schedule?
+Yes, many EMT positions offer part-time or flexible scheduling options. This flexibility is especially common in non-emergency medical transport services and certain healthcare facilities. It allows EMTs to balance their work with other commitments.
What are the physical demands of being an EMT?
+Being an EMT can be physically demanding. It requires lifting and moving patients, often in challenging environments. EMTs must be in good physical condition to handle these tasks safely. Regular fitness and strength training are recommended to maintain the necessary physical capabilities.
Are there any age restrictions for becoming an EMT?
+Age restrictions for becoming an EMT can vary by state and employer. However, most EMT training programs require students to be at least 18 years old. Some programs may have additional age requirements, so it’s important to check with the specific program or state regulations.
Can I pursue further education after becoming an EMT?
+Absolutely! Many EMTs choose to further their education and pursue advanced certifications or degrees. With additional education, EMTs can become paramedics, nurse practitioners, or even physicians. Continuing education opens up new career paths and opportunities for growth.
