What Is College Credit

College credit is a fundamental concept in higher education that represents the value or weight assigned to a course or academic achievement. It is a measurement used by educational institutions to quantify the time and effort required to complete a particular academic task or course. College credits are a crucial aspect of a student's academic journey, as they determine the progress made towards earning a degree or certificate.
In this blog post, we will delve into the world of college credits, exploring their significance, how they are earned, and their impact on a student's academic career. Whether you are a prospective student, a current undergraduate, or simply curious about the educational system, understanding college credits is essential for navigating the path to academic success.
Understanding the Basics of College Credit

College credits, often referred to as "credit hours" or simply "credits," are a unit of measurement used to assess the intensity and duration of a course or academic program. They provide a standardized way to evaluate the workload and academic rigor associated with different courses.
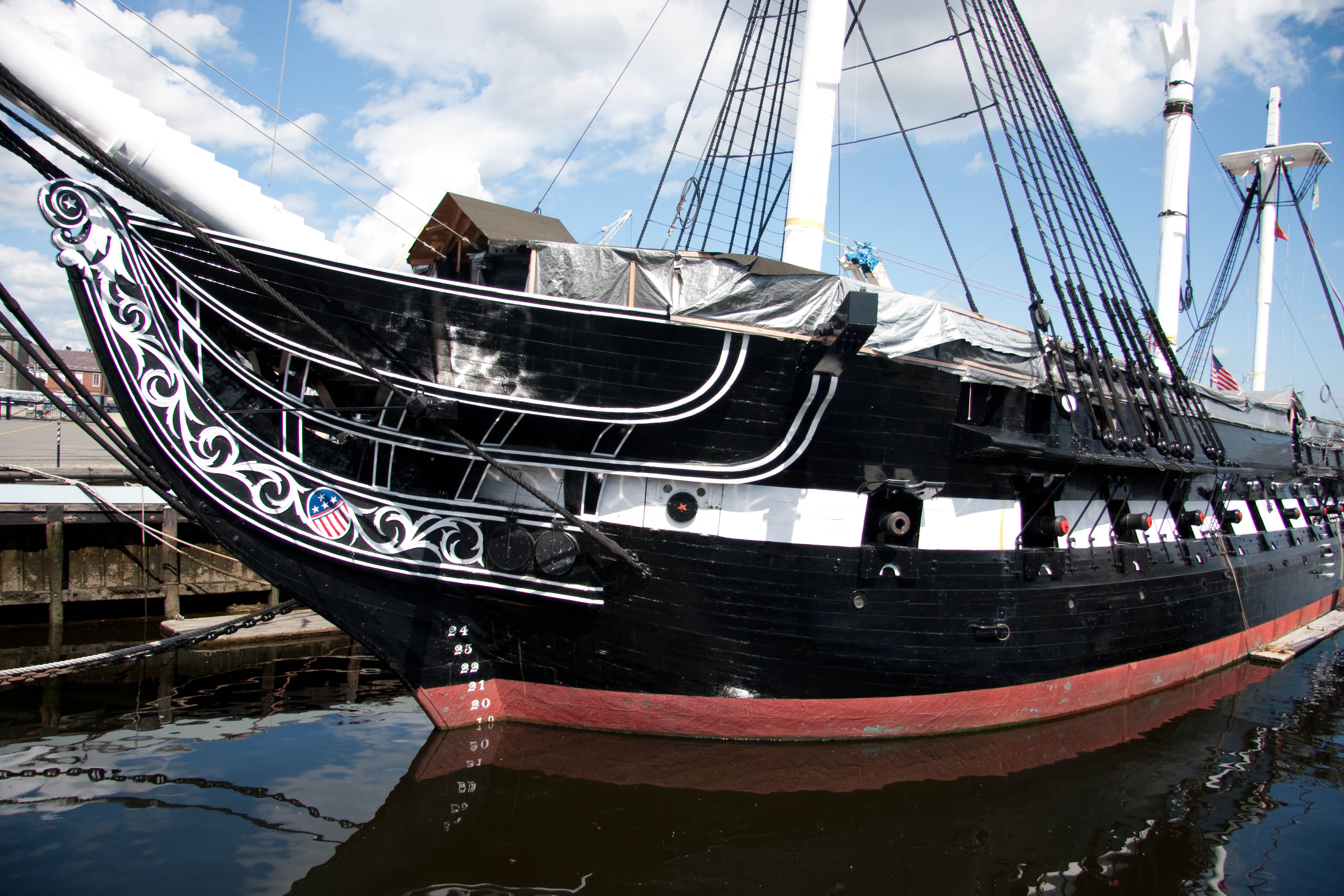
Each credit hour typically represents one hour of class time per week over a standard semester or quarter system. This means that a three-credit course usually meets for three hours per week throughout the semester. However, it's important to note that the credit system can vary slightly between institutions and educational systems.
The number of credits required to complete a degree varies depending on the program and the institution. For example, an associate's degree typically requires around 60 credits, while a bachelor's degree often demands 120 credits or more. These credit requirements ensure that students gain a comprehensive and well-rounded education.
Earning College Credits

Students can earn college credits by successfully completing courses and meeting the academic requirements set by their institution. Here are some common ways to earn college credits:
- Traditional Classroom Courses: Attending and participating in lectures, completing assignments, and passing exams are key to earning credits for traditional classroom courses.
- Online Courses: With the rise of online learning, students can now earn credits by taking courses remotely. These courses often have similar requirements to traditional courses, including assignments, discussions, and exams.
- Transfer Credits: If you have completed courses at another accredited institution, you may be able to transfer those credits to your current college or university. This can save time and money by reducing the number of courses you need to take.
- Advanced Placement (AP) Credits: High school students who excel in AP courses can earn college credits by taking and passing AP exams. This allows them to skip certain introductory courses in college, providing a head start on their degree.
- Dual Enrollment: Some high schools offer dual enrollment programs, allowing students to take college-level courses while still in high school. These courses can earn both high school and college credits, giving students a jump-start on their post-secondary education.
- Credit by Examination: Certain institutions offer credit by examination programs, such as CLEP (College-Level Examination Program) or DSST (DANTES Subject Standardized Tests). Students can earn credits by passing standardized exams, demonstrating their knowledge of specific subjects.
The Importance of College Credits
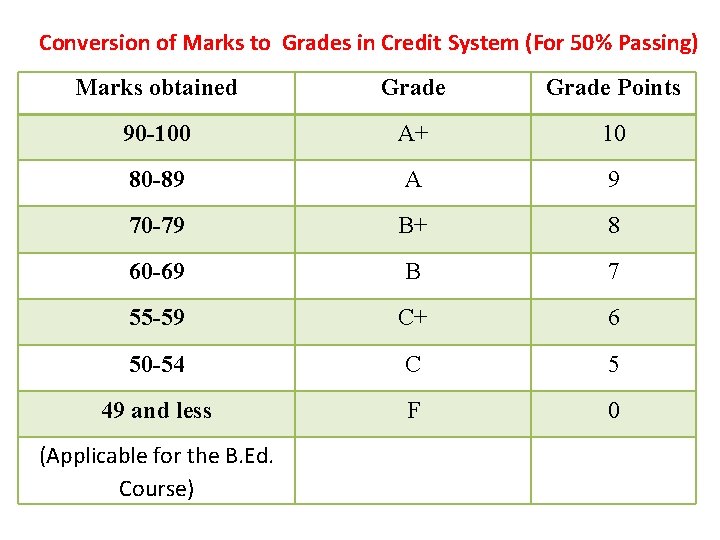
College credits play a vital role in a student's academic journey for several reasons:
- Degree Completion: College credits are the building blocks of a degree. By accumulating the required number of credits, students can successfully complete their chosen program and earn their degree.
- Academic Progress: Earning college credits allows students to track their academic progress. It provides a clear indication of how far they have come and how much further they need to go to reach their educational goals.
- Transferability: College credits are often transferable between institutions. This means that if a student decides to change schools, they can potentially bring their earned credits with them, reducing the time and cost of obtaining a degree.
- Academic Planning: Understanding the credit requirements for a degree helps students plan their academic journey effectively. They can choose courses strategically, ensuring they meet the necessary credit requirements and explore areas of interest.
- Scholarships and Financial Aid: Many scholarships and financial aid programs have credit-based eligibility criteria. By earning and maintaining a certain number of credits, students may become eligible for various funding opportunities.
Tips for Maximizing College Credits

Here are some tips to help you make the most of your college credits:
- Know Your Institution's Credit Policies: Familiarize yourself with the credit policies and requirements of your college or university. This includes understanding the credit transfer process, course prerequisites, and any specific credit-earning opportunities they offer.
- Create an Academic Plan: Work with your academic advisor to create a comprehensive academic plan. This plan should outline the courses you need to take, the credits required for each, and any potential opportunities to accelerate your progress.
- Explore Credit-Earning Options: Consider taking advantage of credit-earning opportunities such as AP courses, dual enrollment, or credit by examination programs. These options can help you earn credits efficiently and potentially reduce the overall time and cost of your degree.
- Maintain Good Academic Standing: Ensure you maintain good academic standing by consistently performing well in your courses. This will not only help you earn credits but also open up opportunities for scholarships and other academic achievements.
- Seek Academic Support: If you encounter difficulties in a course, don't hesitate to seek academic support. Many institutions offer tutoring services, study groups, and other resources to help students succeed and earn their credits.
Transferring College Credits

Transferring college credits is a common practice, especially for students who change institutions or pursue multiple degrees. Here's what you need to know about transferring credits:
- Credit Transfer Policies: Each institution has its own set of credit transfer policies. It's crucial to understand these policies, as they determine which credits will be accepted and how they will be applied to your new program.
- Course Equivalency: When transferring credits, institutions often look for course equivalency. This means that the courses you completed at your previous institution must align with the curriculum and requirements of your new program.
- Credit Limit: Some institutions may have a limit on the number of credits that can be transferred. This limit ensures that students complete a certain portion of their degree at the new institution, promoting a well-rounded educational experience.
- Evaluation Process: The credit transfer process typically involves an evaluation of your transcripts and course descriptions. The receiving institution will assess whether the courses you completed meet their academic standards and requirements.
- Transfer Credit Appeals: If your credits are not automatically accepted, you may have the opportunity to appeal the decision. This process often involves providing additional information or documentation to support the transfer of specific credits.
Common Challenges and Solutions

While college credits are an essential part of the academic journey, students may encounter challenges along the way. Here are some common challenges and potential solutions:
- Course Prerequisites: Some courses have specific prerequisites, meaning you must have completed certain other courses before enrolling. If you find yourself lacking the necessary prerequisites, consider taking the required courses or seeking guidance from your academic advisor to find alternative options.
- Course Overload: Taking too many courses at once can lead to overwhelming workloads and potential academic difficulties. It's important to strike a balance and not overload your schedule. Consult with your advisor to create a manageable course load that aligns with your academic goals.
- Course Availability: Certain courses may not be offered every semester or may have limited enrollment. If you find yourself unable to register for a required course, reach out to your advisor or the department offering the course to explore alternative options or potential solutions.
- Grade Performance: Maintaining good grades is crucial for earning college credits. If you're struggling in a course, seek academic support, attend office hours, and consider forming study groups with peers. Staying proactive can help improve your grade performance and ensure you earn the necessary credits.
The Role of College Credits in Academic Success

College credits are not just a means to an end; they are a vital component of academic success. By earning and managing your college credits effectively, you can:
- Progress efficiently through your degree program.
- Explore diverse subjects and areas of interest.
- Build a strong academic foundation.
- Increase your chances of graduating on time.
- Save time and money by transferring credits or earning them through alternative methods.
Remember, college credits are a tool to help you achieve your academic goals. By understanding how they work and utilizing them strategically, you can make the most of your educational journey and set yourself up for success.
Conclusion: Navigating the World of College Credits

College credits are the currency of higher education, representing the dedication and hard work put into earning a degree. Understanding the concept of college credits, how they are earned, and their impact on your academic journey is essential for making informed decisions about your education. Whether you're a first-year student or considering a transfer, knowing the ins and outs of college credits will empower you to take control of your academic future.
As you navigate the world of college credits, remember to stay organized, seek guidance from academic advisors, and explore the various credit-earning opportunities available. By doing so, you'll be well on your way to a successful and fulfilling academic experience.
Frequently Asked Questions

How many credits do I need to graduate with a bachelor’s degree?
+The number of credits required for a bachelor’s degree can vary depending on the institution and program. On average, a bachelor’s degree typically requires around 120 credits. However, it’s important to check with your specific institution for their credit requirements.
Can I transfer credits from a community college to a four-year university?
+Yes, it is often possible to transfer credits from a community college to a four-year university. Many institutions have transfer agreements in place to facilitate the process. However, it’s crucial to research the transfer policies of both institutions and ensure that your credits will be accepted.
What happens if I fail a course and lose my credits?
+If you fail a course, you may lose the credits associated with it. However, some institutions offer opportunities to retake the course and potentially regain the credits. It’s important to consult with your academic advisor to understand your options and the potential impact on your degree progress.
Are there any online platforms that offer college credits for free?
+While there are online platforms that offer free educational resources, earning college credits typically requires enrollment in accredited institutions. However, some institutions may offer free or low-cost online courses that can lead to credit transfer or credit by examination opportunities.
Can I earn college credits through work experience or internships?
+Yes, some institutions recognize work experience and internships as a way to earn college credits. This is often done through prior learning assessment programs, where your knowledge and skills gained through work are evaluated and translated into academic credits. Check with your institution to see if they offer such programs.



